The heart of any vehicle is its engine, a complex piece of machinery that converts fuel into energy to power the car. Understanding how a car engine works can help us appreciate the engineering marvel that enables us to travel long distances with ease.
At its most basic level, a car engine is a heat engine that operates on the principle of the internal combustion process. This means that fuel is burned inside the engine to produce heat, which is then converted into mechanical energy to move the vehicle.
The Four-Stroke Cycle
Most modern car engines operate on a four-stroke cycle, which consists of four distinct stages: intake, compression, power, and exhaust.
- Intake: In this stage, the piston moves downward, creating a vacuum that draws in a mixture of air and fuel through the intake valve. The fuel is usually injected into the air stream or delivered by a carburetor.
- Compression: As the piston moves upward, it compresses the air-fuel mixture. This compression increases the pressure and temperature of the mixture, making it easier to ignite.
- Power: At the top of the compression stroke, a spark plug ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture, causing a rapid expansion of gases. This explosion forces the piston downward, generating mechanical energy that is transferred to the crankshaft.
- Exhaust: After the power stroke, the piston moves upward again, pushing the burned gases out of the engine through the exhaust valve.
This four-stroke cycle repeats continuously as long as the engine is running, providing the power needed to propel the vehicle.
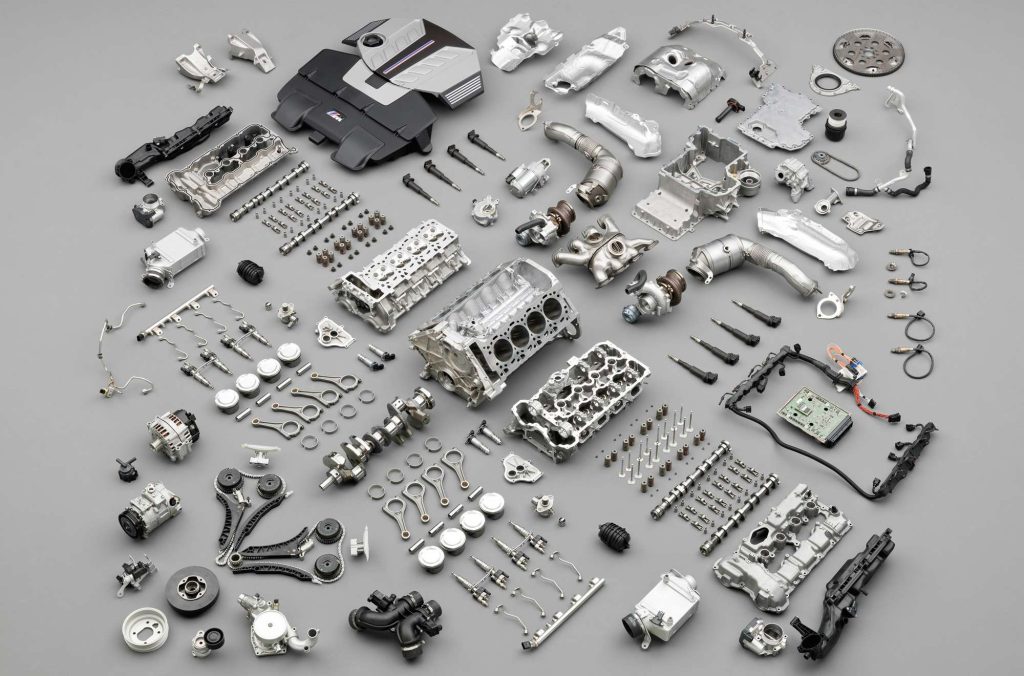
Key Components of a Car Engine
Several key components work together to make the engine operate smoothly. These include:
- Cylinder Block: The cylinder block is the main body of the engine and contains the cylinders where the combustion process takes place. It also houses the pistons, connecting rods, and crankshaft.
- Pistons: Pistons are cylindrical components that move up and down inside the cylinders. They are connected to the crankshaft by connecting rods and transfer the force of the combustion explosion to the crankshaft.
- Connecting Rods: Connecting rods connect the pistons to the crankshaft and transmit the force of the piston’s movement to the crankshaft.
- Crankshaft: The crankshaft converts the up-and-down motion of the pistons into rotational motion. This rotational energy is then transmitted to the transmission and wheels to propel the vehicle.
- Valves: Valves control the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and the exhaust gases out of the engine. Intake valves allow the air-fuel mixture to enter, while exhaust valves release the burned gases.
- Spark Plugs: Spark plugs provide the spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture at the appropriate time in the combustion cycle.

Fuel Delivery and Ignition Systems
The fuel delivery system is responsible for supplying the engine with the right amount of fuel at the right time. This can be done through various methods, such as fuel injection or carburetion.
The ignition system, on the other hand, is responsible for creating the spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture. This can be achieved through traditional spark plugs or more advanced ignition systems like direct ignition.
Cooling and Lubrication Systems
As the engine operates, it generates a significant amount of heat. The cooling system, which typically consists of a radiator, water pump, and coolant, is responsible for removing this heat to prevent the engine from overheating.
The lubrication system, meanwhile, supplies oil to the moving parts of the engine to reduce friction and wear. This helps to ensure the longevity and smooth operation of the engine.
In conclusion, understanding the working principle of a car engine is essential for anyone interested in automobiles. From the four-stroke cycle to the various components and systems that make up the engine, there is a lot of technology and engineering that goes into making a car engine run smoothly. Whether you’re a car enthusiast or just curious about how things work, learning about car engines can be a fascinating and rewarding experience.

































Discussion about this post